On November 8, 2021, The Department of Health & Human Services (HHS), Office of Inspector General (OIG) released a revised and renamed Provider Self-Disclosure Protocol (SDP), now known as the “Health Care Fraud Self Disclosure “protocol. The SDP was created in 1998, and the protocol can be used to voluntarily identify, disclose and resolve instances of potential fraud involving federal healthcare programs. As described on the OIG website, “Self-disclosures give persons the opportunity to avoid the costs and disruptions associated with a Government-directed investigation and civil or administrative litigation.”Continue reading
OIG Unveils Latest Tool for Evaluating Fraud Risk

By: Karina Gonzalez
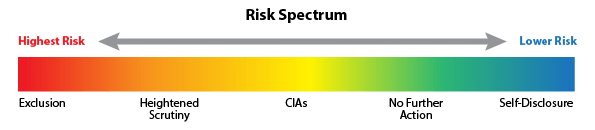
The Office of Inspector General (OIG) announced the launch of a new tool on its website titled the “Fraud Risk Indicator”. The OIG has stated that the purpose for the tool is to provide guidance on how it has evaluated risk in settling False Claims Act (FCA) cases and to publicize information about where FCA defendants fall on the OIG’s risk spectrum. This tool can benefit patients, healthcare industry professionals and other individuals who may find this information relevant. This tool will also benefit the public with information about providers charged under the FCA that are at high risk for committing healthcare fraud. The Indicator shows the Risk Spectrum from Highest Risk to Lower Risk.Continue reading
Healthcare Compliance: Providers Must Use Plans They Have in Place
 By: Jacqueline Bain
By: Jacqueline Bain
In 2015, Assistant Attorney General Leslie Caldwell spoke publicly about the importance for every healthcare provider to not only have a compliance program on its shelf, but also being sure that the compliance program is “tailored to the unique needs, risks and structure of each business or industry.” Assistant Attorney General Caldwell explained, “the adequacy of a compliance program is a factor when [the DOJ] decide[s] how and whether to prosecute a company. The lack or insufficiency of a compliance program can have real consequences for a company when a violation of law is discovered.”Continue reading
The Final Overpayment Rule and Practical Steps for Compliance
By: James Saling
On February 11, 2016, the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) issued the final overpayment rule commonly referred to as the “60 Day Rule”. Physicians, labs, hospitals, and other providers that receive reimbursement under Part A or B must comply with the 60 Day Rule or face penalties under the False Claims Act.
The 60 Day Rule requires that overpayments (e.g., payment for coding errors) be reported and returned to CMS within 60 days after the date on which the overpayment was identified. Identification of the overpayment was addressed at length in the regulation. The 60-day clock to identify overpayments starts ticking “when the person has, or should have through the exercise of reasonable diligence, determined that the person has received an overpayment and quantified the amount of the overpayment.” Reasonable diligence means that the provider takes steps to uncover overpayments and steps to quantify the amount of the overpayment.Continue reading
CMS Sanctions Cigna over Substantial Failures in Medicare Plans
 By: Karina Gonzalez
By: Karina Gonzalez
Centers for Medicare and Medical Services (CMS) has banned Cigna from enrolling and selling new Medicare products because of issues with Part C (Medicare Advantage Plans) and Part D (Prescription Drug Program )that increased enrollees out-of-pocket expenses which led to delays or denials in receiving medical services and prescription drugs. These sanctions were imposed effective 1/21/2016 because CMS determined that “Cigna’s conduct posed a serious threat to the health and safety of Medicare beneficiaries.” Continue reading
Provider Credit Balances Result in $6.8 Million Overpayment Settlement
 By: Karina Gonzalez
By: Karina Gonzalez
USA v. Pediatric Services of America – settlement under the False Claims Act involving a health provider’s failure to investigate credit balances on its books to determine whether they resulted from overpayment by a federal health care program.
The U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Georgia announced that Pediatric Services of America Healthcare, Pediatric Services of America, Inc., Pediatric Healthcare, Inc., Pediatric Home Nursing Services (collectively, “PSA”), and Portfolio Logic, LLC agreed to pay $6.88 million ($6,882,387) to resolve allegations that PSA, a provider of home nursing services to medically fragile children, knowingly (1) failed to disclose and return overpayments that it received from federal health care programs such as Medicare and Medicaid, (2) submitted claims under the Georgia Pediatric Program for home nursing care without documenting the requisite monthly supervisory visits by a registered nurse, and (3) submitted claims to federal health care programs that overstated the length of time their staff had provided services, which resulted in PSA being overpaid.
“Participants in federal health care programs are required to actively investigate whether they have received overpayments and, if so, promptly return the overpayments,” said United States Attorney, John Horn. “This settlement is the first of its kind and reflects the serious obligations of health care providers to be responsible stewards of public health funds.”Continue reading
Governing Boards in Healthcare Organizations – Making Compliance Your Priority
 By: Jackie Bain
By: Jackie Bain
Does your healthcare entity have a governing Board? How involved is that Board in overseeing your business? Would your Board members be able to respond to questions about your business’ compliance-related activities? Recently, the Office of the Inspector General (“OIG”), in conjunction with a host of non-profit healthcare associations, released guidance on achieving compliance for healthcare governing boards. The guidance is not based on abstract principals of compliance, instead it points to applicable federal law, OIG guidance, case law, and sentencing guidelines.
Each and every healthcare organization, whether or not it accepts reimbursement from government payors, must have in place regulatory compliance measures designed to protect the population it serves, and the persons paying for and providing those services. All levels of a healthcare organization must be cognizant of their roles in the organization’s continuing commitment to compliance. Even Board members, who often do not experience the inner-workings of the entities they represent, have an obligation and duty to the organization to act in a manner that stressed compliance. Applicable federal and state laws, how they apply to an organization, and how the organization reacts to its obligations imposed by those laws, must be of paramount importance to a governing Board.
The OIG compliance guidance for healthcare Boards tracks 4 areas over which boards should have specific oversight:Continue reading
The 7 Essential Elements of an Effective Compliance Plan
 By: Jackie Bain
By: Jackie Bain
When a healthcare provider cares for a patient, many times, the provider will set out directives for the patient to follow in order to live a healthier life. These changes may include changes in lifestyle, eating habits, and obedience in taking medications. A patient’s compliance with these directives instructs the provider on how to care for the patient in the future. A patient who does not follow these directives may suffer health consequences.
Similarly, the government sets out legal regulations for healthcare providers. The government expects healthcare providers to comply with its regulations, and providers who don’t can suffer consequences as a result. The regulations governing health care providers are vast and dynamic. In order to keep abreast of the changes in law, and to evidence an intent to comply with law, healthcare providers should strongly consider instituting compliance programs in their businesses.
Compliance with healthcare laws is important. Any number of consequences can result in the event that a healthcare provider is out of compliance—the most devastating being that the Department of Health and Human Services Office of the Inspector General (“OIG”) has the authority to exclude healthcare providers from participation in Medicare and other federal health care programs. Ignorance of the law does not absolve a healthcare provider of liability.Continue reading