By: Sharon Parsley
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) relies on its Medicare Administrative Contractors (MACs) to serve as guardians of the Medicare trust fund through the MACs taking steps to prevent improper payments. Despite that reliance, in its most recent report to the US Senate Finance Committee, the Government Accountability Organization (GAO) reports that improper payments totaling $41.1 billion (no, that is NOT a typo, that is a “b”) occurred during 2016 in the Medicare fee-for-service program [1]. That figure represents an overall 11% percent improper payment rate.
How many of us would feel good about being “wrong” in our core job function 11% of the time? Not very many of us, I suspect.
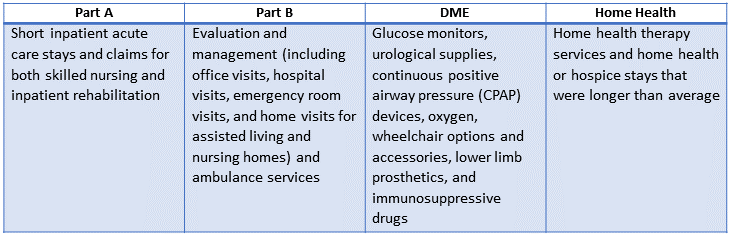
The GAO report goes on to quote the MACs as generally having ongoing concerns about the following types of claims as those which pose the greatest financial risk to the Medicare trust fund.
| Part A |
Part B |
DME |
Home Health |
| Short inpatient acute care stays and claims for both skilled nursing and inpatient rehabilitation |
Evaluation and management (including office visits, hospital visits, emergency room visits, and home visits for assisted living and nursing homes) and ambulance services |
Glucose monitors, urological supplies, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) devices, oxygen, wheelchair options and accessories, lower limb prosthetics, and immunosuppressive drugs |
Home health therapy services and home health or hospice stays that were longer than average |
So, what does CMS plan to do to hold its MACs more accountable and to further the objective of reducing improper payments? On August 14th CMS announced an expansion of an ongoing pilot program “Targeted Probe and Educate” Medical Reviews (TPE).
7 Things to Know
The basics of what the provider and supplier communities need to know about the TPE program follows.
- The silver lining here is that providers and suppliers with minimal aggregated billing pattern deviations from their peer group coupled with good audit track records may now experience fewer MAC medical review audit requests.
- TPE will be concentrated on providers and suppliers with “the highest claim error rates or billing practices that vary significantly from their peers”[1].
- In the first round of reviews, MACs will review a 20-40 record probe sample of claims for each lucky provider or supplier selected to participate in TPE.
- Providers and suppliers who perform well during the first TPE audit, or who demonstrate significant improvement during the second or third audit may be removed from the TPE audit cycle for a period of up to 12 months.
- Each provider and supplier with moderate and high error rates during round one TPE audits will receive provider-specific education, be given approximately 45 days to improve its rate of compliance, and will advance to a bonus round two TPE audit.
- Providers and suppliers who fail to improve during the round two TPE audit will again receive provider-specific education, be given another 45 days to improve processes and controls to improve rates of compliance, and will advance to the third round of TPE audits.
- Providers and suppliers who perform poorly during the final TPE audit round could be placed on 100% prepayment review, be subject to the dreaded “extrapolation”, and/or be referred to the appropriate Recovery Auditor, Zone Program Integrity Contractor or a Unified Program Integrity Contractor. It goes without saying that none of these are desirable outcomes.
7 Steps to Readiness
- Many providers and suppliers are outliers relative to some component of their billing pattern. Use all the resources at your disposal to “know your numbers” and where your areas of exposure or risk most likely exist.
- Closely review results and findings from any recent internal audits or reviews conducted pursuant to your compliance program.
- If you have experienced recent external medical review audits, evaluate those results. If there were denied claims, identify the issue or issues leading to the denials. Then, identify the root causes of errors. Finally, and most importantly, resolve the problems which lead to denied claims.
- If you provide health care services in any of the areas mentioned above which are deemed highest risk by the MACs, examine on your billing patterns in those service lines.
- Pay attention to what your MAC says about TPE and areas of emphasis for audit. If you provide those health care services, examine your billing in those areas.
- Drill down into any area where your billing pattern materially deviates from your peer group and make sure you understand the basis for the deviation.
- If there is no obvious business rationale or justification for a considerable deviation from the “norm” do a deeper dive of your charge capture and billing practices to determine whether any process or practice needs further evaluation and/or adjustment.
These suggestions should position you for a successful outcome if / when you are selected to participate in the TPE audit program.


 By:
By: 

 By:
By:  Just the other day CMS issued new rules and temporary waivers to help combat the COVID pandemic. We are getting flooded with questions about
Just the other day CMS issued new rules and temporary waivers to help combat the COVID pandemic. We are getting flooded with questions about 
 By:
By: 
 By:
By: 
 By: Urgent Medical Billing, Guest Contributor
By: Urgent Medical Billing, Guest Contributor